What Is Bitcoin DeFi: The Rise of BTCFi
For years after its introduction in 2009, the Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain remained an environment used exclusively for asset transfers and storage. The rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) on Ethereum (ETH) as an alternative to traditional financial systems in 2017–2018 seemed to ignore Bitcoin, the world's oldest blockchain, and its vast potential. Many at that time assumed that Bitcoin's relevance in the industry would decline, as smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) elevated the status of Ethereum. However, it didn't take long for the Bitcoin community to come back with answers, some utilizing sidechains and other Layer 2 solutions, and others leveraging the chain's own native mechanisms.
In the past few years, the ecosystem of apps and decentralized platforms that enable Bitcoin-focused DeFi — or BTCFi, as it's come to be known — has flourished. BTCFi is now a growing world, featuring efficient payment solutions, smart contract sidechains, fungible token protocols and even a technology for issuing Bitcoin-based NFTs.
The exciting world of BTCFi still lacks the sophistication and programmability muscle of Ethereum's DeFi sector, but it's catching up fast. In this review, we’ll take a closer look at some of the critical apps and platforms that power BTCFi, a sector that leverages the potential of the world's largest crypto asset, the BTC coin. We’ll also discuss the key differences between the emerging BTCFi ecosystem and the established Ethereum DeFi universe.
Key Takeaways:
Bitcoin's DeFi ecosystem, known as BTCFi, is made up of a variety of projects that utilize smart sidechains, scalable payment solutions, processing engines compatible with both Bitcoin and Ethereum, wrapped token solutions and native Bitcoin NFTs.
Some of the major projects are Taproot Assets, BitVM, Bitlayer, Bitcoin Ordinals and the Runes protocol.
The development of the BTCFi ecosystem was turbocharged after Bitcoin's Taproot upgrade in November 2021.
Understanding Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The launch of Ethereum in 2015 is often considered the starting point for the DeFi industry. For the first time, a popular smart contract–capable blockchain arrived on the scene, opening up opportunities for DeFi solutions such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending and borrowing protocols, and other crypto-based finance operations. However, it wasn't until 2017–2018 that the DeFi field really took off, with the introduction of pioneering protocols like Aave (AAVE), Uniswap (UNI), Curve Finance (CRV) and Compound (COMP), among others.
These DApps and their business models were made possible thanks to Ethereum's smart contract functionality, which enabled complex logic and transaction execution capabilities on the blockchain through the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) computational engine.
While early DeFi protocols represented a wide variety of niches, five areas quickly emerged as the most popular and dominant within the overall DeFi ecosystem:
DEX platforms, particularly those based on the automated market maker (AMM) liquidity pool model, which facilitated efficient asset swap operations
Lending and borrowing protocols, which established thriving user-to-user and user-to-liquidity pool markets for lending and borrowing crypto assets
Crypto derivatives trading platforms
Automated yield management solutions
Algorithmic stablecoin issuance protocols
A few years later, another major category — staking and liquid staking, including liquid restaking solutions — also became a prominent niche within the DeFi industry.
What Is Bitcoin DeFi?
Bitcoin missed the early DeFi revolution, largely due to its absence of native smart contract capabilities. However, as early as 2018 and 2019, the first solutions aimed at enabling Bitcoin-based DeFi, or BTCFi, began to emerge. Some of these projects revolved around smart contract–capable Layer 2 sidechains linked to the Bitcoin network. Others championed the idea of wrapped tokens (e.g., wrapped Bitcoin, or WBTC) that could be transferred to Ethereum and used within this chain's leading protocols, such as AAVE, Curve Finance and Compound for collateral provision, swaps and other popular DeFi transactions.
The BTCFi field received a major boost in November 2021 with the introduction of Bitcoin's Taproot upgrade, which introduced the functionality of batching multiple digital signatures for processing. These signatures are used on Bitcoin to verify transactions. Taproot’s practical advantages include significantly improved transaction processing and less bloat on the network. As a result, more complex transactions could be processed in less time and with more modest block space requirements. In turn, the ability to process more transactions in a more complex way led to a flurry of BTCFi activity and the emergence of new projects on the network.
In the past couple of years, newer BTCFi projects — such as BitVM, Bitlayer, Bitcoin Ordinals and the Runes protocol — have further advanced the sector, bringing it much closer to Ethereum's still dominant DeFi capabilities.
Bitcoin DeFi vs. Ethereum DeFi
Compared to Ethereum's giant DeFi ecosystem, BTCFi is still a small world. However, BTCFi is catching up quickly, despite its somewhat late start. Below are some of the key points that distinguish Bitcoin DeFi from Ethereum DeFi:
BTCFi features fewer digital assets and lower liquidity levels than Ethereum DeFi. This may limit the choice of solutions and products for DeFi traders. At the same time, it could represent unique opportunities in an environment that’s less congested and competitive than Ethereum’s.
BTCFi apps are often based on non–smart contract technologies. While smart contracts are at the heart of Ethereum DeFi apps, many BTCFi solutions are based on workarounds that eliminate or limit the need for full smart contract functionality.
BTCFi enjoys the acclaimed security of the Bitcoin blockchain. While Ethereum is also known for its solid security record, Bitcoin's proof of work (PoW) block validation mechanism is widely believed to be more secure, even if less efficient, than Ethereum's proof of stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
BTCFi apps may feature lower interoperability with other smart contract blockchains as compared to Ethereum DeFi apps. However, there are some solutions — e.g., wrapped tokens and computational engines with EVM compatibility — that are designed to eloquently address this issue.
Smart contract solutions for BTCFi aren’t native to Bitcoin. The main smart contract solutions for BTCFi are based on using sidechains with smart contract functionalities, or add-on computational engines such as BitVM. In contrast, Ethereum relies on its built-in EVM engine.
Bitcoin DeFi Platforms and Projects
Taproot Assets
Launched in July 2024 by the Lighting Labs team, who also created Lightning Network (which we'll cover shortly), Taproot Assets is a protocol built on the Taproot upgrade that enables the issuance and transfer of a wide variety of crypto assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. These assets are stored within unspent transaction outputs (UTXO), and can easily be transferred as part of standard Bitcoin transactions. The protocol stores the metadata off-chain to reduce the load on the Bitcoin network.
While Taproot Assets was originally built to facilitate stablecoin settlement on Bitcoin, users can now use it to create all kinds of assets on Bitcoin, including both fungible tokens and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). These assets can easily be transferred as part of regular Bitcoin transactions, and can also be issued and transferred within Lightning Network for low-cost, highly scalable transfers, thereby running little risk of congesting the Bitcoin network.
Lightning Network
Lighting Network is used not only for Taproot Assets transfers, but also for a wide variety of Bitcoin transactions. Launched in 2018 by Lightning Labs, this Layer 2 solution lets users transact much more efficiently and cost-effectively as compared to native Bitcoin transfers. When two transacting parties use Lightning Network, the platform establishes a dedicated one-to-one channel for them for efficient communication. The parties commit to the channel by first bonding an amount of BTC on the underlying Bitcoin blockchain to open the channel. Then, the channel is opened and can be used for transacting, with all of the transactions processed off-chain.
The off-chain transaction mode allows Lightning Network to swiftly process a large amount of transfers at low cost, thus avoiding delays and high fees typically associated with the Bitcoin network. In fact, some of the most popular use cases for this solution are for micropayments and high-volume transfers.
BitVM
Ethereum's DApp functionality has been supported by the blockchain's processing engine — EVM. For years, Bitcoin lacked a processing engine that would support programming logic and smart contracts. This all changed with the introduction of BitVM in late 2023.
BitVM is a computational engine that’s designed to enable Turing-complete programming logic on Bitcoin. This opens up the opportunity to directly create DApps with advanced functionality and logic on the blockchain. While BitVM supports somewhat sophisticated programming logic for Bitcoin, it has one key limitation — the engine natively supports only two-party interactivity.
This limits, to a certain degree, the kind of DApps that can be used with BitVM. Any solutions that require only two-way interactions (e.g., one-to-one payment systems), can work well with the engine. However, more complex DApps, which normally require multi-party transactional ability, can't natively be accommodated by BitVM. Despite this limitation, BitVM is one of the key innovations opening up ways to create functional DApps on Bitcoin.
Stacks
Stacks (STX) is a Layer 2 solution that’s capable of hosting fully-fledged smart contract functionality and DApps on Bitcoin, as well as leveraging Bitcoin for security and settlement. This allows DApps hosted on Stacks to utilize the network's smart functionality while benefiting from the security of Bitcoin’s PoW network.
Stacks has its own block validation model, called proof of transfer (PoX). Stacks' blocks are anchored to Bitcoin, with the latter ultimately used for transaction validation. Using its anchor to Bitcoin, Stacks settles all transactions on Bitcoin via periodically transferred batches.
Ordinals
One area in which smart contracts have been used extensively on Ethereum is for NFTs. Due to Bitcoin’s lack of native smart functionality, its environment had been deprived of NFTs up until early 2023. That’s when developer Casey Rodarmor introduced the Ordinals protocol, a unique way of creating NFT-like assets on Bitcoin without using smart contracts.
Rodarmor noted that each satoshi — the smallest unit of a Bitcoin — on the network can be uniquely identified from its position within each mined block. The Ordinals protocol specifies a way to inscribe pieces of data (e.g., text or image) into a uniquely identifiable satoshi, essentially opening up a route to creating Bitcoin-based distinct digital artifacts, such as NFTs.
As of mid-September 2024, the Ordinals protocol remains the primary way to create Bitcoin NFTs. The total number of these digital artifacts on Bitcoin’s network is approximately 75 million.
Runes
Runes is another innovative technology introduced by Casey Rodarmor for the Bitcoin ecosystem. In the section on Taproot Assets above, we noted how that protocol leverages Bitcoin UTXOs to create tokens. The Runes protocol works similarly at the basic level and is also compatible with Lightning Network.
Runes establishes a way to create fungible crypto assets on Bitcoin by attaching key token properties to Bitcoin UTXOs. However, there are significant differences between Taproot Assets and Runes. Unlike Taproot Assets, which stores token metadata off-chain, Runes is a purely on-chain solution. It's been lauded as a highly secure and lightweight way to handle fungible crypto assets on the Bitcoin chain.
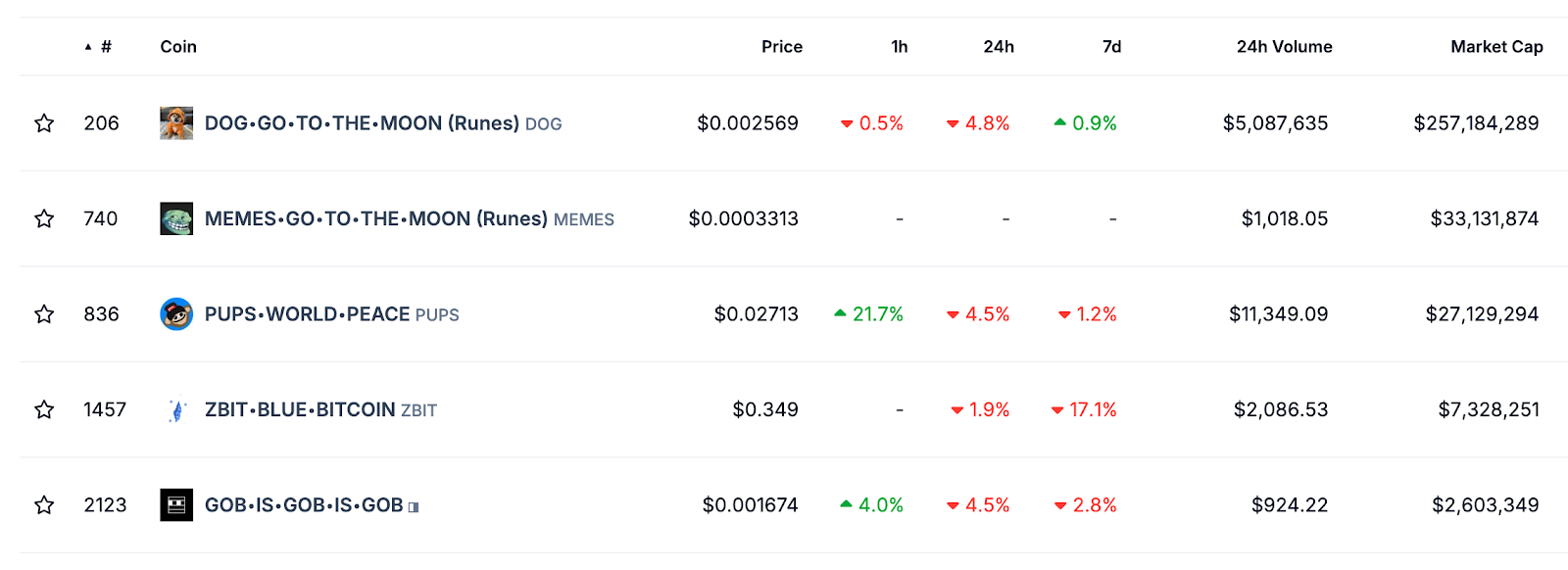
As of mid-September 2024, there are close to 100,000 Runes tokens in existence, with the leading token, DOG•GO•TO•THE•MOON (DOG), having amassed a market cap of around $257 million. The majority of popular Runes tokens are classified as meme coins.
Bitlayer
Bitlayer is a Layer 2 blockchain platform that leverages the BitVM engine described above. It represents the first widely known implementation of BitVM technology. Bitlayer acts as a processing medium that handles transactions and then settles them on the underlying Bitcoin chain. The platform, however, isn't just about BitVM — it also features a high degree of compatibility with the Ethereum ecosystem. Using its Layered Virtual Machine (LVM) technology, Bitlayer makes it easy to port Ethereum-based solutions to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Programming code written in an EVM-compatible language like Solidity or Vyper easily compiles into a Bitlayer-compliant format, which greatly simplifies DApp porting and communicating between the Ethereum and Bitlayer environments. As such, Bitlayer is among the few platforms that enjoy both 100% EVM compatibility and the much-heralded security of Bitcoin.
Rootstock (RSK)
Rootstock (RSK) is a Layer 2 solution that combines EVM compatibility with Bitcoin's security protection. With its mainnet launch dating back to January 2018, Rootstock is the oldest Layer 2 sidechain servicing Bitcoin. It features smart contract functionality, and is one of the key ways for developers to launch and operate Bitcoin-linked DApps.
The Rootstock blockchain's primary crypto asset, RBTC, is pegged to BTC at a rate of 1:1. Users can transfer their BTC to Rootstock, which then converts it to RBTC for use within the platform's ecosystem. At any time, users can reclaim their BTC and transfer funds back to Bitcoin. Besides smart contract functionality, what sets Rootstock apart from the native Bitcoin chain is its superior scalability and lower transaction costs. For instance, while the standard block confirmation time on Bitcoin is about 10 minutes, it's just 30 seconds on Rootstock.
Rootstock’s shorter transaction confirmation time and full EVM compatibility make it an excellent environment for DApps to tap into the potential of the BTC ecosystem. At the same time, the platform has specifically focused its efforts on enabling DeFi use cases and attracting partner projects in the niche of decentralized trading.
Liquid Network
Like Rootstock, Liquid Network is another longtimer among Bitcoin Layer 2 platforms. It launched its mainnet in September 2018, and has proven to be among the leading solutions to address Bitcoin's high transaction costs and poor scalability. As with Rootstock, Liquid Network is a Bitcoin sidechain that maintains a BTC-pegged asset, Liquid Bitcoin (L-BTC). Users can swap their BTC for L-BTC and then use the funds within Liquid Network's ecosystem for faster and more reliable asset transfers.
However, similarities between the two sidechains end here. Unlike Rootstock, Liquid Network has no native smart contract functionality. Its platform is designed primarily to improve the scalability and costs of asset transfers and to issue stablecoin assets. Like Lightning Network, it focuses on payments and transfers. The difference, however, is that Lightning Network is optimized for small or micro transfers, while Liquid Network is more suitable for medium and large asset transfers.
BadgerDAO
BadgerDAO (BADGER) is a leading DeFi platform that has championed the concept of linking the Bitcoin and Ethereum worlds. Launched on Ethereum, Badger’s key platform leverages wrapped Bitcoin assets, such as RENBTC and WBTC, across Ethereum's rich ecosystem of DeFi apps. While not a native Bitcoin solution, Badger plays a vital role in expanding the utility of BTC to additional ecosystems beyond the Bitcoin network.
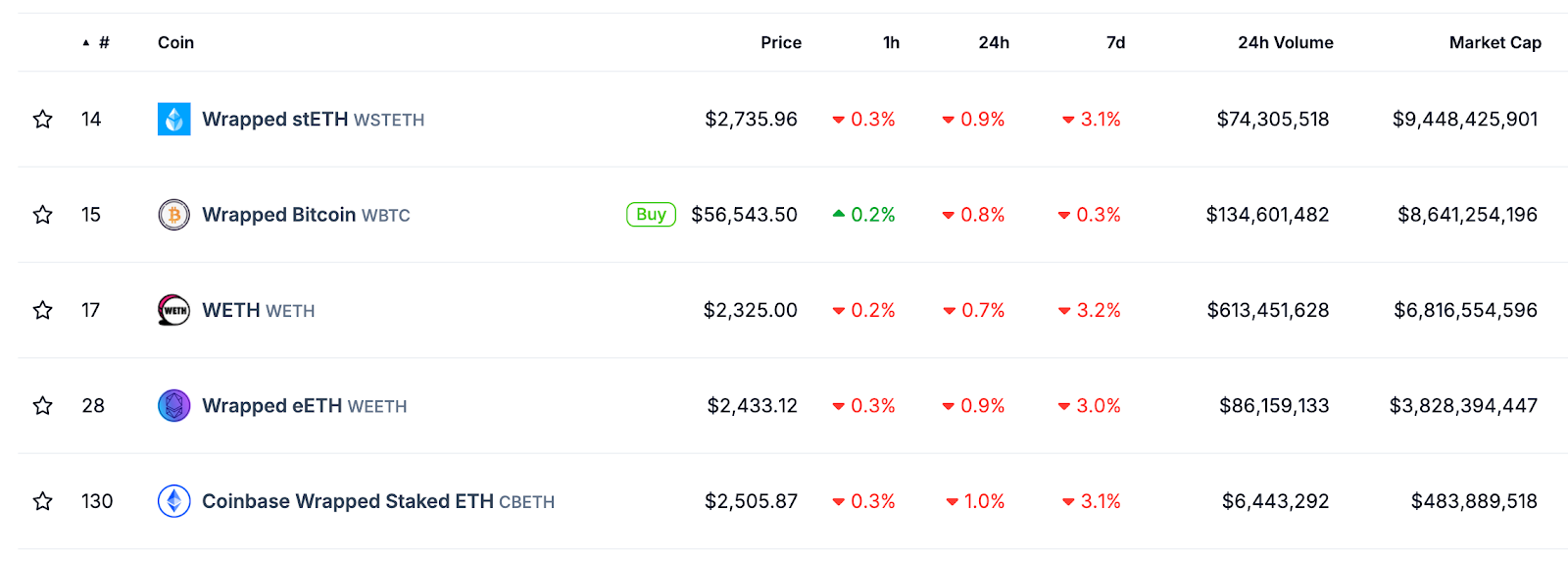
BTC (or rather its wrapped variations) is used on Badger as a form of collateral for DeFi operations. Badger offers a dedicated bridging solution, the Badger Bridge, to easily transfer BTC to the platform wrapped as one of the two popular wrapped tokens — RenBTC or WBTC. These tokens can then be used in various DeFi apps to earn yield or act as collateral. Both of the wrapped Bitcoin tokens supported by Badger are quite popular, although RenBTC is a less prominent player in the field than WBTC. Currently the second-highest-capped wrapped token in the industry, WBTC enjoys vast popularity with a market cap of $8.6 billion.
Advantages of Bitcoin DeFi
Bitcoin DeFi apps offer several distinct advantages to traders, developers and project operators. First, there's the security factor — Bitcoin is considered a highly secure environment even by the stringent standards of the blockchain industry. Arguably, Bitcoin has an advantage in this area, compared to Ethereum and most other smart contract chains. Secondly, since BTCFi is a less mature and overcrowded environment than Ethereum DeFi, there are unique opportunities for traders to benefit from its less efficient markets.
The third advantage is relevant specifically for NFT enthusiasts. Unlike Ethereum NFTs, which store their artwork or other media off-chain while the tokens’ metadata is kept on Ethereum, Bitcoin NFTs — supported by the Ordinals protocol — are stored fully on-chain. All of the metadata and actual media files related to an NFT are kept on Bitcoin. This provides benefits both in terms of security and greater intellectual rights protection.
Finally, BTCFi offers developers and operators a unique benefit: Since BTCFi is an emerging area, there are opportunities to present first-of-its-kind solutions for the ecosystem — something that’s considerably harder to do in the cutthroat world of Ethereum DeFi.
Security and Risks in Bitcoin DeFi
Despite Bitcoin's well-regarded security, BTCFi does have its risks. Some BTCFi solutions rely heavily on off-chain processing, or on the use of sidechains. These environments may not have the same security profile as Bitcoin itself. Secondly, lower liquidity levels may increase losses, due to higher slippage rates and other market inefficiencies.
Thirdly, the smaller ecosystem of DApps may limit your choice of trading platforms. In addition, the use of wrapped tokens essentially moves your BTC assets to other blockchain ecosystems, which may not be as secure as the Bitcoin chain. There are, of course, also additional transaction costs due to the need to wrap and unwrap tokens.
The Future of Bitcoin DeFi
BTCFi continues to develop and mature, with newer projects like Ordinals and Runes at the forefront of its development. As the BTCFi ecosystem of apps and solutions grows, there will likely be more opportunities in the future for cross-chain transactions and interoperability with other blockchain environments.
While there are solutions bringing together the worlds of Ethereum and Bitcoin, the BTCFi field has yet to expand to other prominent ecosystems, such as the system of Polkadot (DOT) parachains and the network of Cosmos (ATOM) blockchains. Later in 2024 and in the following few years, we’re likely to see the emergence of such cross-ecosystem solutions as well.
Closing Thoughts
BTCFi is a fast-developing sector, with solutions that leverage smart contract sidechains, wrapped tokens, Taproot upgrade–charged asset management solutions, native Bitcoin NFTs and add-on engines capable of EVM compatibility. The projects we've covered above are some of the most fundamental BTCFi players and true pioneers of this field.
Naturally, there's still a need for BTCFi to grow larger and offer more diversity and sophistication to traders. This is all happening now, right in front of our eyes. While the current BTCFi ecosystem can’t yet rival that of Ethereum's DeFi, let's not forget one factor that points to its vast potential — the massive funds held in BTC, which still represent well over 50% of the entire crypto market capitalization.
#LearnWithBybit